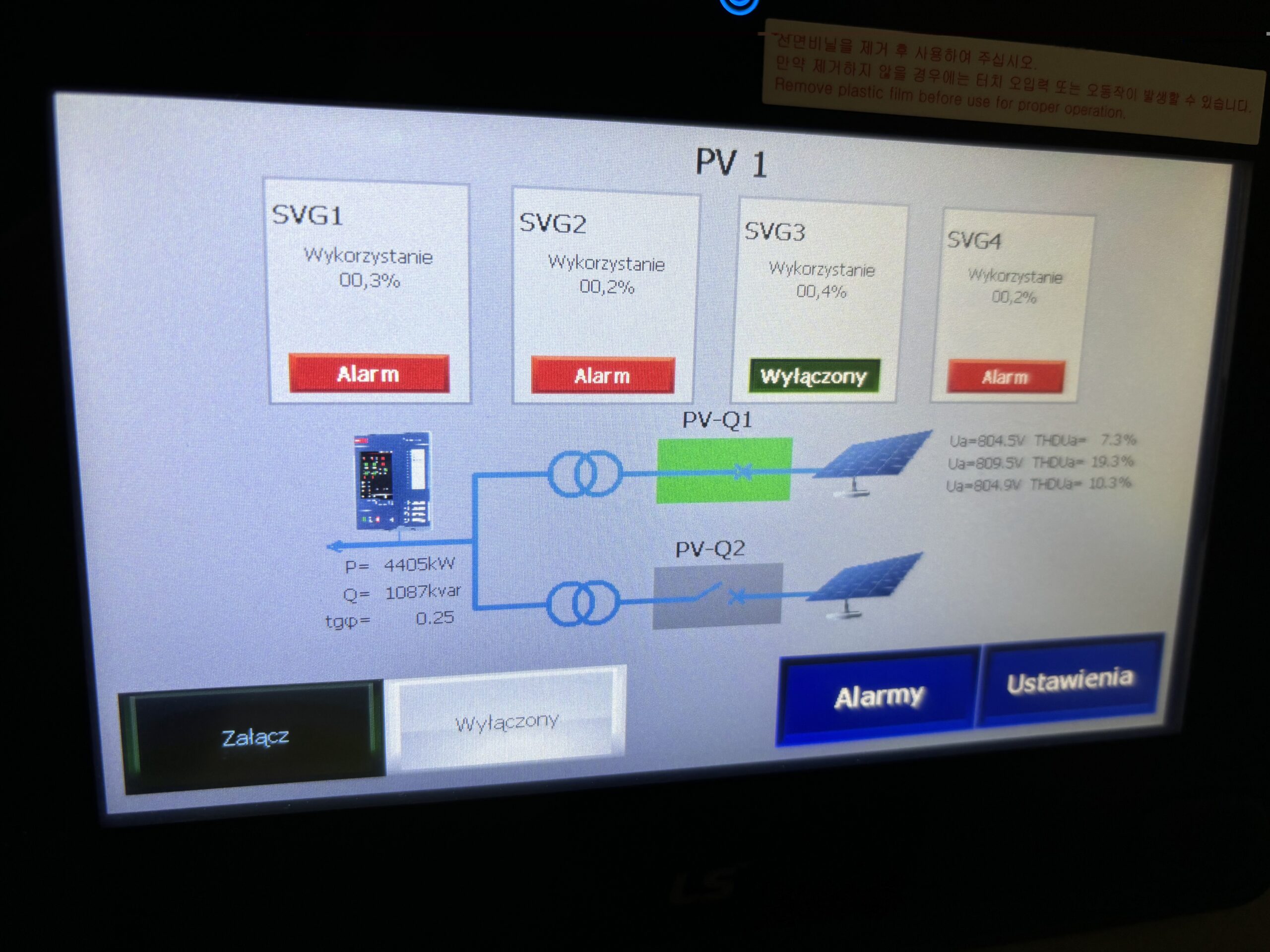
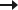The ANIRO team carried out a comprehensive implementation of a reactive power compensation system at one of the large District Heating Companies (PEC) in Poland. The goal of the project was to increase energy efficiency and improve the quality of power parameters, particularly achieving an optimal power factor cos φ of 0.99. Below we present a detailed description of the solution and its effects.


Analysis of needs and technical challenges
The project began with a detailed analysis of the energy needs of the PEC, as well as the technical conditions of the existing power supply infrastructure. This specific facility had two medium-voltage power supply fields that supplied equipment with high active and reactive power requirements. Additionally, one of the fields was loaded by a combined heat and power (CHP) generator, which provided active power at a level of 3.2 MW.
The reactive power consumption in some circuits reached levels that significantly affected the quality of supply and the stability of network parameters, which is why it was necessary to implement an advanced reactive power compensation system.
Technical solution
A key element of the implemented solution was the installation of two active SVG compensators, each with a power of 800 kVar, manufactured by SINEXCEL. These compensators were powered through 15/0.4 kV transformers with a Dyn5 connection group and a capacity of 1250 kVA each.
Current measurement and control
Current measurement was carried out using medium-voltage transformers 300/5, which allowed for precise monitoring of power parameters. Each power supply field was equipped with two-winding transformers: one winding was designated for the energy meter, while the other was for protection and compensation.
Power factor optimization
Thanks to the use of SVG compensators, a stable power factor of cos φ = 0.99 was achieved on both power supply circuits. The first power supply field, to which the combined heat and power (CHP) generator was connected, showed an active power level of 3.2 MW. Thanks to the compensation, full power supply stability was achieved. In the second power supply field, which drew active power and inductive reactive power with a tangent of power factor (tg) of over 2, approximately 160 kW and nearly 400 kVar, compensation enabled the reduction of reactive power and the maintenance of a stable power factor.
Results and benefits
The implemented solution yielded tangible results for both the PEC facility and the network operator:
– Improved stability of power parameters – a constant power factor of cos φ 0.99 significantly reduces costs associated with reactive power consumption.
– Network protection against overloads – precise reactive power compensation reduces overloads, extending the lifespan of the energy infrastructure.
– Optimization of generator operation – the implemented compensators allowed for stable operation of the combined heat and power (CHP) generator while ensuring the required active and reactive power parameters.
Summary
The reactive power compensation project implemented by ANIRO at one of the large District Heating Companies (PEC) in Poland is an example of the application of advanced technology in optimizing power parameters. Efficiency and stability of the system were achieved through the precisely selected SVG active compensators and the implementation of advanced measurement solutions. This is another step by ANIRO towards providing modern solutions in the field of energy quality, tailored to the specific needs of the client.

 Previous
Previous